What Are Beacons and How Beacons Technology Works
November 16, 2021

Introduction
If you own a business or do marketing-related jobs you may have heard of Beacon technology. Perhaps you even received a Beacon from Google as part of Beacon Project, a Google program that sends free Beacons to businesses for the purpose of improving visibility and mobile experience.
Beacon technology has come a long way since Apple launched in 2013 and is expected to continue to evolve. This year, Global Market Insights predicts that the Beacon technology market will surpass $25 billion by 2024.
We have seen its significant impact on the Internet of Things (IoT) as well as modern marketing models. As such, a good understanding of how they work and what they are for would go a long way towards providing you with the edge to take advantage of the technology. In this blog, we will be talking about what beacon technology is, what role it plays in IoT and Big Data, and how it can shape the future of advanced technology.
What is Beacon Technology?
In a word, beacons are specialized computing systems that are meant to fulfill very specific functions. Broadly speaking, they are proximity transmitters that are often the size of your standard modem. They make use of Bluetooth wireless technology to connect various devices together, either within the beacon network itself or external IoT devices. Beacons use proximity technology to detect human presence nearby and trigger preset actions to deliver informational, contextual, and personalized experiences.
Brief History: Where Did Beacon Technology Begin?
The history of Beacon began a long time ago, a technology closely related to the Internet of Things (loT), starting with Bluetooth and accelerated with the advancement of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), now known as Bluetooth Smart.
The Bluetooth protocol (invented by the telecommunications service provider Ericsson in 1994) has existed for many years, allowing the wireless transmission of data including audio and video by creating a wireless personal network with shareable data.
In 2010, BLE was part of Bluetooth 4.0, released with a focus on transferring simple link URLs and small amounts of analog data, rather than live video and audio. It is called Low power because the protocol is adapted to be less battery-intensive, which opens up a lot of possibilities in the future.
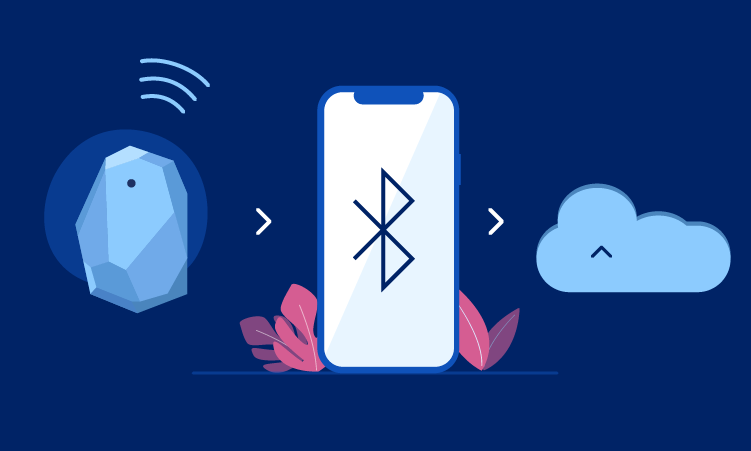

A beacon is a piece of hardware that emits a BLE signal to a Bluetooth-enabled receiver, allowing another device to determine how close the transmitter is. When we talk about machine-to-machine (M2M) communication, this is what we really mean in regards to Beacon BLE communication.
A Beacon doesn’t load content, it simply transmits a signal that allows the user of the user’s phone or tablet to find out how close the Beacon is. The assets (e.g. a coupon, promotion, voucher) will be delivered exclusively to the user application (For example, the Facebook Beacon app distributes Facebook ads in the respective area)
The limitations of GPS in indoor environments include the inability to navigate or locate using GPS and so Beacon and BLE have combined to fill that gap.
How Do Beacons Work?
The Beacon device is very simple. Each device contains a CPU, radio, and battery, and it works by continuously emitting an identifier (ID). This identifier is picked up by your device, usually a mobile phone, and marks an important place in the environment. The Identifier is a unique ID number that your smartphone recognizes and is unique to the Beacon. Once connected, Beacon will perform any function it has programmed including advertising, navigation, and tracking.
Beacon’s working mechanism is a mini-computer the size of a Wi-Fi router. It is an indoor navigation system that uses proximity technology to search for human presence around and perform established actions to deliver contextual, informative, and personalized experiences. When a user walks around the area where this indoor navigation system is located, the Beacon will send a code to the user’s mobile device via text message.
We can consider a good example of advertising in a mall.
Step 1: Users search in Google about “Red Lipstick”.
Step 2: Your Google search ad appears.
Step 3: The user clicks on the search ad, browses the product, then goes to the store to view the product.
Step 4: Users decide they want to try on shoes before they buy, so they walk into your store.
Step 5: When they enter the store, their phone receives an ID identification number from the store Beacon.
Step 6: Beacon recognizes this phone as the same phone that clicked on their search ad and associates this data with your Google Ads account as a web store visit.
By logging physical store visits from your search ads, this technology helps you understand the impact and performance of your search ads. If you find they are driving a lot of traffic to your store, you may want to invest more in search and media advertising.
Classification of Beacon
IBeacon is a BLE protocol released by Apple in December 2013, this is the first official set of BLE protocols most all beacons support. This protocol is supported only on iOS, but can now be found very easily. Many API functions support searching for Beacons on Android. An application is required to search for beacons and perform operations with them. Beacon supports two types of monitoring interactions (monitoring) and coverage (ranging). With monitoring mode the app will alert even if the app has turned off monitoring mode, range mode only works while the app is running. With iBeacon, what data will the beacons emit? They broadcast three messages: UUID, Major, and Minor. There will never be two beacons with the same UUID, Major, and Minor.
Eddystone is a BLE protocol announced by Google in July 2015, officially supported on both iOS and Android platforms. It is an open protocol and supports many different packets of information and data. Unlike iBeacon, Eddystone only supports one main basic interaction — the “Eddystone discovery”, which is a similar concept to iBeacon ranging. This interaction is contained within three different data packet types — the Eddystone UID, Eddystone URL and, Eddystone TLM. The Eddystone UID is a data packet that can trigger push notifications or app action.
In contrast, the Eddystone URL sends an actual URL. The data is simple and doesn’t need an app to work. Lastly, Eddystone TLM is used to manage beacons and includes information such as battery and voltage, beacon temperature, number of packages sent, and beacon uptime. TLM is sent alongside the other two packet types and acts as meta-data about the beacon.
Where is the Application of Beacon?
Beacon technology has a lot of expansion in the future, so its use is still under development. For now, the main focus remains on navigation and advertising. This is where you can see companies investing heavily at the moment.
Overall, Beacon can be applied quite widely in many industries and fields:
- Manufacturing
- Supply Chain Management
- Wholesale, retail/commercial
- Restaurant Hotel
- Travel travel
- Education
- Health care
Although proximity marketing and inventory management are two top areas used by small to medium business owners, several sub-segments demonstrate a rapid growth rate. Sub-sectors with the largest growth potential include:
- Cloud: Cloud-based beacons help companies oversee multiple cloud-hosted services used on smart devices. They reduce costs while providing infrastructure security.
- Education: BLE beacon technology supports interactive learning zones, easy attendance taking, access to text information, and seamless communication.
- Wi-Fi: Beacon hardware combined with Wi-Fi-based sensors helps customers find their destination and lowers infrastructure costs for enterprises.
Beacon and Big Data

Big Data uses Big Data sets to predict and reveal patterns in human behavior. This is where indoor positioning and positioning can help everything from Marketing to businesses better understand complex situations and respond more appropriately. Here is an example to show how Beacon is included in the Big Data picture of an employee management business.
An employee is issued an ID card that can be used for a number of different purposes.
- Check attendance, entry, and exit
- Deliver lunch to their account when they are available in the cafeteria
- Sick leave
- Book a meeting room
- Heatmap measurement
- Navigating, guiding when there is fire, explosion, accident in the building
- Process management, movement in the factory
From the data obtained from a person – that person’s ID, the company can combine information about their movements, whom they meet, and cross-reference with other members of their team. It is then possible to find out if this person can request a seat move to be closer to another member of the group if the suspected illness can reduce their diet, if they may need a taxi because they work late they may require a larger meeting budget.
Another example is in a factory when tracking the movement of workers in the production process, we can measure and evaluate the optimized working process, but we cannot apply methods to more optimized work. This requires long-term data collection and evaluation.
Conclusion: The Future Of Beacons
So, what is the future of beacon technology? As already mentioned, the industry is forecasted to be worth quite a lot of money in the coming years. However, from a more general standpoint, beacon technology is set to take over pretty much all forms of retail and shipping industries going forward.
More than just that, we have concluded that marketing is also getting a considerable boost from beacon technology. There have been numerous instances where beacons were used by companies in order to monitor customer patterns of behavior that would aid them in improving their branding. After all, beacons demand little to invest, are easy to set up and manage regardless of business scale, and bring clear, straightforward benefits to business across industries. Why not leverage them?
Keep reading about
LEAVE A COMMENT
We really appreciate your interest in our ideas. Feel free to share anything that comes to your mind.